 1.
Fixed Ratio Schedule
1.
Fixed Ratio Schedule
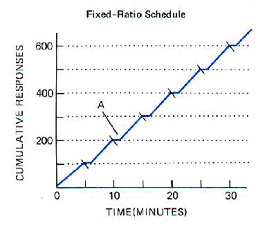
Description: A reinforcer is given after a specified number of correct responses.
This schedule is used to increase and maintain a steady rate of specific responses.
It is the best schedule for learning a new behavior.
Produces:
- A high steady rate until reinforced
- A post-reinforcement pause
- Ratio strain with large increases in the response requirement
- High RTE
Examples in natural environments:
- Jobs that pay based on units delivered. Employees often find this schedule
undesirable because it produces a rate of response that leaves them nervous
and exhausted at the end of the day. They may feel pressured not to slow down
or take rest breaks, since they feel that such will costs them money. This
is an example of how a schedule can produce a high rate of response even though
the response rate is aversive to the subject.
Examples in video games
- Collecting tokens. Many games require the player to collect a fixed number
of tokens to advance to the next level, obtain a new life point, or receive
some other reinforcer.
- Attaining a new level in an RPG. Some RPG's clearly indicate how much experience
is required to achieve the next level. A high degree of certainty as to the
level of work that will be required to achieve the next level puts the player
on a fixed ratio schedule.
 1.
Fixed Ratio Schedule
1.
Fixed Ratio Schedule 1.
Fixed Ratio Schedule
1.
Fixed Ratio Schedule